It takes just a few numbers to put into perspective the total economic impact of the global industrial asset base. While coming up with a clear value for the world’s combined industrial asset base turns out to be quite difficult, the World Bank says that the value-added of the global industrial sector (including verticals like aerospace, electricity, manufacturing, mining, etc.) was in the range of $29T in 2024. More to the point, for the purposes of this discussion, the global market for industrial asset management was estimated at $ 159B in 2023, forecast to rise to $506B by 2030. All of which leads to the indisputable conclusion that maintaining your asset base is a critical strategic imperative for any industrial firm—large, small, or someplace in between.
What if industrial asset owners don’t get it right?
Inadequate asset Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) practices can have significant and widespread consequences, resulting mainly from operational disruptions and significant financial outcomes.
Operational Consequences
Inefficient or poorly performed MRO can affect core business operations by reducing asset performance and process stability.
- Increased Unplanned Downtime: Equipment failures due to neglect or reactive maintenance halt production. For a large automotive plant, an hour of downtime can cost up to $2.3M.
- Reduced Asset Reliability and Lifespan: Improperly maintained equipment operates sub-optimally and wears out faster, shortening effective life and requiring costly, premature replacement.
- Reduced Product Quality: Poorly maintained assets often lead to defective products, which can mean costly rework, scrap, or even product recalls, damaging a company’s brand reputation.
- Reactive Maintenance: Poor MRO practices can force maintenance staff into a reactive mode, where emergency repairs replace scheduled, proactive work. This strains resources and can even increase the probability of future failures.
- Supply Chain Disruption: Unplanned asset failures often lead to unpredictable demand for spare parts, resulting in rushed, overpriced spot purchases, emergency freight costs, and challenges meeting production schedules and customer deadlines.
- Safety and Compliance Risks: Poor MRO practices can lead to facilities and equipment that are more prone to accidents, compromising worker safety and increasing the risk of regulatory fines and legal liabilities.
Financial Outcomes
The operational consequences described above lead directly to major financial challenges, some of which are hidden or indirect.
- Excessive Maintenance Costs:
- Higher Labor Costs: Unplanned asset repairs frequently require overtime wages, making them more expensive than scheduled work.
- High Acquisition Costs: Ad hoc procurement results in a high volume of small, uncoordinated purchases, which typically means missing out on volume discounts.
-
- High Shipping Costs: Critical part stockouts oblige staff to order on an emergency basis, requiring higher cost expedited shipping and freight expenses.
- Increased Inventory Holding Costs:
-
- Excess and Obsolete Inventory: Poor inventory management can lead to overstocking (20-30% of spares can go unused) and parts duplication, tying up working capital and increasing storage, insurance, and eventual disposal cost.
-
- Stockout Costs: Having insufficient quantities of critical parts on hand can result in higher downtime costs and lost production.
- Revenue Loss and Missed Opportunities: Unplanned downtime translates to lost production volume and possible contractual penalties for missed delivery deadlines.
- Lower Return on Assets (ROA): Shorter equipment lifespans and reduced operating efficiency reduce overall financial return on capital asset investments.
Avathon Autonomy for MRO Operations
Avathon tackles all these challenges by harnessing the power of AI to turn today’s MRO practices from statically planned and reactive to dynamically planned and proactive. Autonomy for MRO Operations enables users to rapidly detect emerging issues, prescribe the most effective actions, and align the entire maintenance ecosystem in real time. Using Avathon’s proprietary computational knowledge graph technology to map assets, resources, schedules, and dependencies, the platform enables AI agents to anticipate maintenance needs, optimize parts and workforce deployment, and coordinate supply chain actions in real time.
Autonomy for MRO’s wide-ranging feature set equips asset managers—whether aircraft, vehicles, manufacturing equipment, or energy providers—to extract the most value from their asset base while minimizing recurring and capital costs.
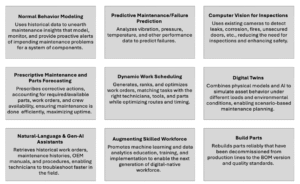
Avathon Autonomy for MRO Feature Set
Conclusion—AI-Enhanced MRO is key to world-beating operational performance
Avathon’s Autonomy for MRO Operations turns traditional MRO operating plans into living, AI-powered systems, delivering immediate, enduring cost savings, efficiency, and improved asset performance. By combining all these platform features into a unified, adaptive plan, operators can significantly reduce operating costs, minimize downtime, and maximize the revenue potential of their capital-intensive asset portfolios.
Click here to download our white paper on Autonomy for MRO Operations.